I used to think strong relationships were built on grand gestures such as vacations, expensive dinners, and anniversary surprises. Over time, I realized something far more practical and far more powerful:
The strongest couples don’t rely on occasional fireworks.
They rely on consistent weekends.
After observing couples I admire and evaluating what has worked in my own life I’ve noticed a couple behaviors that show up again and again. They’re not complicated. They’re intentional.
Here’s what I’ve learned.
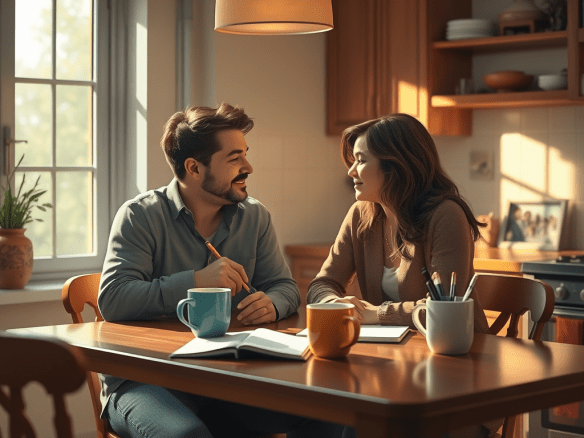

1. We Reset: Together
Weekdays are operational. Work, obligations, responsibilities.
Weekends are relational.
Every Saturday morning, before the noise starts, we check in. Not logistics. Not bills. Not errands.
We ask:
- How are you really doing?
- What felt heavy this week?
- What felt good?
This ritual prevents emotional backlog. In relationship psychology, unresolved micro-tensions accumulate into macro-conflict. Strong couples clear the emotional ledger weekly.
We don’t let small things compound.
2. We Protect Unstructured Time
High-performing couples schedule everything… except presence.
One of the most stabilizing habits we’ve built is blocking out time with no agenda. A walk around the pool. Coffee on the porch. Sitting in silence.
Research from the Gottman Institute shows that couples who build “love maps” detailed knowledge of each other’s inner worlds have higher long-term satisfaction. You don’t build love maps in rushed 10-minute conversations.
You build them in unstructured time.
So we slow down on purpose.
3. We Do Something Hard Together
Shared adversity strengthens bonds.
Whether it’s a workout, tackling a home project, or having a difficult conversation, strong couples lean into productive discomfort side by side.
There’s neuroscience behind this. Oxytocin (bonding hormone) and dopamine (reward pathway) are both activated when partners overcome challenges together. The shared win rewires the relationship positively.
When we sweat together, build together, or solve together, we trust more together.
4. We Disconnect From the World to Reconnect With Each Other
Phones are relationship disruptors.
According to research published in the American Psychological Association journals, perceived partner distraction by devices (often called “technoference”) correlates with lower relationship satisfaction.
So one thing I wish we did every weekend and something more people should consider:
Put your devices away during meals and conversations.
No scrolling. No divided attention.
Attention is the most valuable currency in a relationship.
What I focus on grows.
5. We Reaffirm the Vision
The strongest couples aren’t just surviving the present they are building a shared future.
At least once each weekend, we talk about:
- Goals
- Finances
- Health
- Travel
- What kind of life we’re designing
This habit aligns with principles highlighted in positive psychology research from institutions like Harvard University, where shared meaning and future orientation are strongly correlated with life satisfaction.
We don’t drift.
We design together.

The Bigger Truth
Strong relationships aren’t built in dramatic moments.
They’re built in repeated, deliberate weekends.
I’ve learned that love isn’t sustained by intensity… it’s sustained by consistency.
Every weekend is an opportunity:
- To reconnect
- To repair
- To realign
- To recommit
The couples who thrive aren’t lucky.
They’re disciplined.
And the discipline isn’t complicated.
It’s these small things… repeated every single weekend.